
Increasing success rate and establishing trust in medical education
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality in Medicine: Unique Opportunities for Healthcare Providers, Doctors, Researchers, Residents, Patients, and Chemists
Virtual Reality: Boosting Success Rates and Building Trust in Medical Education
In 2013, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated a global shortage of about 7.2 million healthcare professionals. This shortage is projected to rise to 12.9 million by 2035. Along with the insufficient and uneven distribution of healthcare workers, inadequate educational programs have affected the uniform delivery of healthcare services worldwide. Leading healthcare organizations are striving to develop solutions to increase the workforce and improve the quality and relevance of medical education.

Medical Education Using Virtual Reality
In recent years, various e-learning methods have been employed to transfer knowledge and train medical students, with virtual reality applications gaining significant traction. Virtual Reality Environments (VREs) allow users to experience real-life scenarios through simulations and acquire practical knowledge that might be challenging in real settings.
Here are a few examples of the benefits of VR in medical education:
1. Reducing Stress and Anxiety in Medical Students
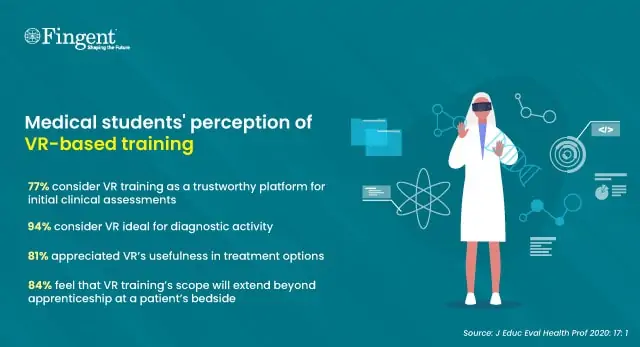
Emergency medical cases and trauma can be intimidating and stressful for inexperienced physicians. Preparing young doctors to handle emergencies before facing real-world situations is a significant challenge. Immersive Virtual Reality (IVR) offers a unique solution for training. Students who underwent VR-based training reported:
Better understanding of anatomical locations
Reduced surgery time in real environments
Enhanced safety for both physicians and patients
Lower costs and educational efforts
2. Seamless Hospital Training
During the strict lockdowns of the COVID-19 pandemic (April-July 2020), medical universities replaced traditional hospital training with virtual reality alternatives.

3. Developing Empathy in VR Environments
VR allows users to experience any situation from different perspectives, earning it the nickname “The Ultimate Empathy Machine.” For example, an educational project at the University of New England used VR tools to teach empathy toward Alzheimer’s patients.
4. Improving Skills and Speed in Operating Rooms
Studies show that physicians who receive simulation-based VR training demonstrate significant improvements in their practical performance.
5. Enhancing Health Awareness Among Patients
Beyond physicians, patients can also benefit from VR to better understand their health conditions. For instance, they can visualize the impacts of unhealthy habits like smoking or obesity on their well-being.

Getting Started with Virtual Reality
VR in medicine is no longer a science fiction concept. Physicians trained with VR report better outcomes compared to traditional methods. From hosting engaging medical conferences to alleviating labor pain and speeding up recovery in physiotherapy, this technology is revolutionizing the future of medicine.
Source: Fingent

Manshour Fanavari Arian
Science and Technology Park Office: Mashhad, 12th kilometer of the Asian Highway, Khorasan Science and Technology Park, Technology and Knowledge-Based Institutions Building